-
Spastic Diplegia and Increased Functional Mobility
What is the best clinical management for children with cerebral palsy- spastic diplegia when increased functional mobility is the identified outcome?
Clinical Scenario: Cerebral palsy (CP) is the most frequently reported diagnosis for children who receive physical therapy, with spastic CP being the most common.
Clinical Bottom Line: In an outpatient setting, frequency and duration of PT should be individualized and based on child and family needs. Periodic and episodic care is used in the management of children with spastic diplegia. Intensity of services may be higher for children with increased impairment or those who undergo surgery. Regardless of intervention environment, each session should be designed to meet the learning style/abilities of the child and family, provide meaningful activities to achieve child and family needs, and be integrated into the child and family routines to achieve success.
Search: Google scholar
Search terms: child, cerebral palsy, physical therapy/procedures, practice guidelines
Citation: O’Niel, M., et al. Physical Therapy Clinical Management Recommendations for Children with Cerebral Palsy- Spastic Diplegia: Achieving Functional Mobility Outcomes. Pediatric Physical Therapy 2006; 18:49-72.
Study Summary:
- Examination of functional mobility
- Patient history
- Systems Review
- Tests and Measures (See Appendix A)
- Musculoskeletal System
- ROM, strength testing, alignment and posture, growth
- Neuromuscular System
- Balance, muscle tone, sensory/motor function
- Cardiopulmonary System
- Endurance, pulmonary/cardiac function
- Musculoskeletal System
- Evaluation and Physical Therapy Diagnosis
- The evaluation reflects the examiner’s hypotheses for the basis of the child and family’s needs related to the child’s current movement problems. The diagnosis is the primary movement problem that has brought the child/family to seek PT services and is the focus of the planned episode of care.
- Prognosis and Plan of Care
- Trahan and Malouin reported on the use of intermittent intensive intervention: 4 times per week for 4 weeks, followed by 8 weeks of no therapy; showed improvements in gross motor function in children with CP.
- Intervention
- Coordination, Communication and Documentation
- Patient-Related Instruction
- Procedural Intervention
- To demonstrate an increase in strength, recommendations include two to three times per week for 6-10 weeks at 65% of maximum isometric strength or between 3-10 repetitions maximum
- To improve cardio respiratory endurance, 30 to 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous intensity physical activity, three to six times per week is recommended
- For younger children, a goal of 10-15 minutes of intense activity interspersed with recreational games for 30 to 45 minutes for 2 sessions a week
- Re-examination: If goals are achieved, then the child is discharged from service and maybe be referred to community agency/resources for recreation or other physical activity services. If goals are only partially achieved or not achieved, then the POC for the child and family is revised and services may be continued if appropriate.
Appraisal: Pros- Recommendations help therapists develop systematic approaches to service delivery and documentation that will contribute to evidence-based practice and enhanced outcomes.
Cons- Limited research findings are available to determine the optimal amount of intervention required for the best/most effective function outcomes for children with cerebral palsy.
The Evidence: See Figure 1.
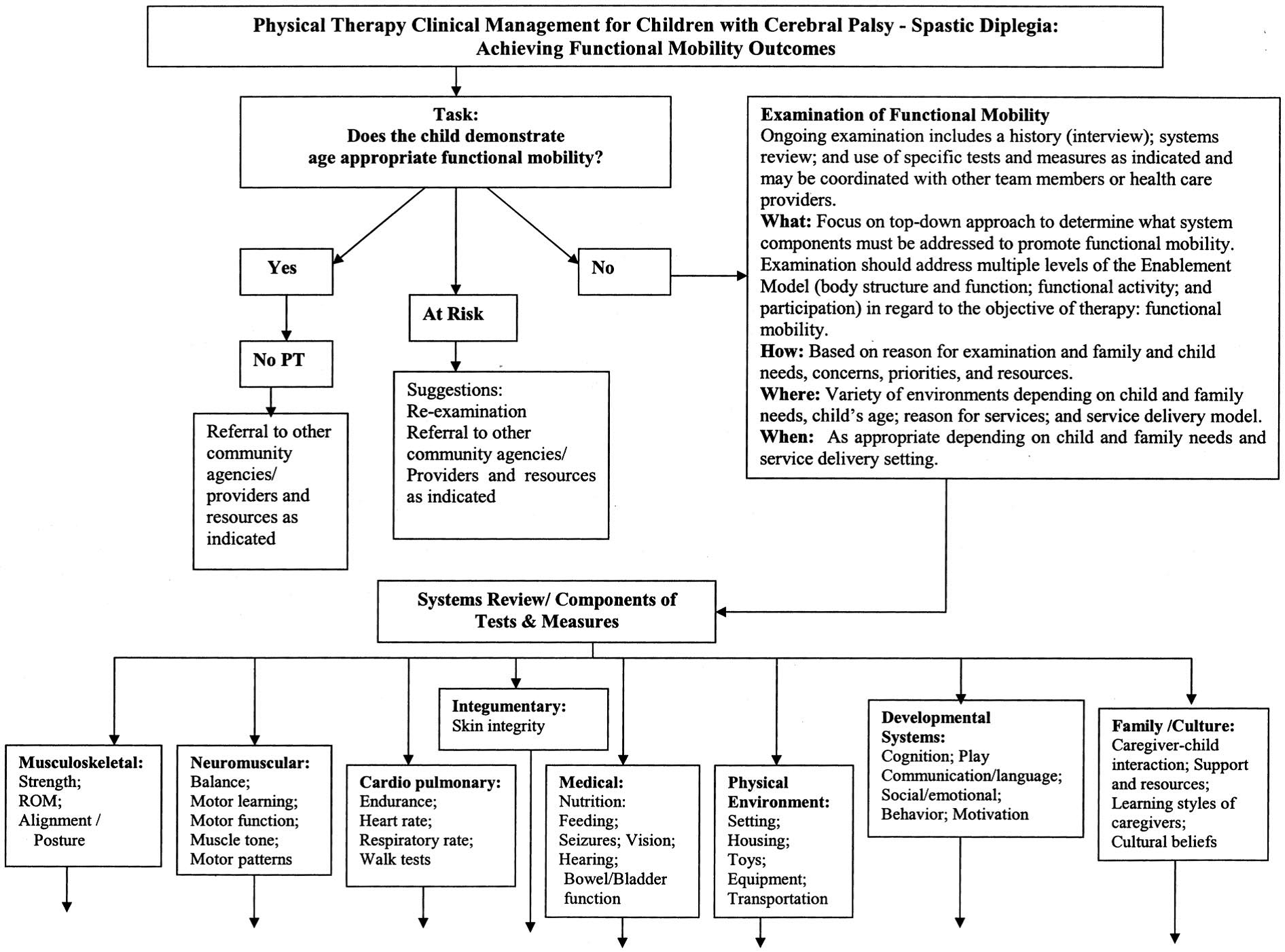
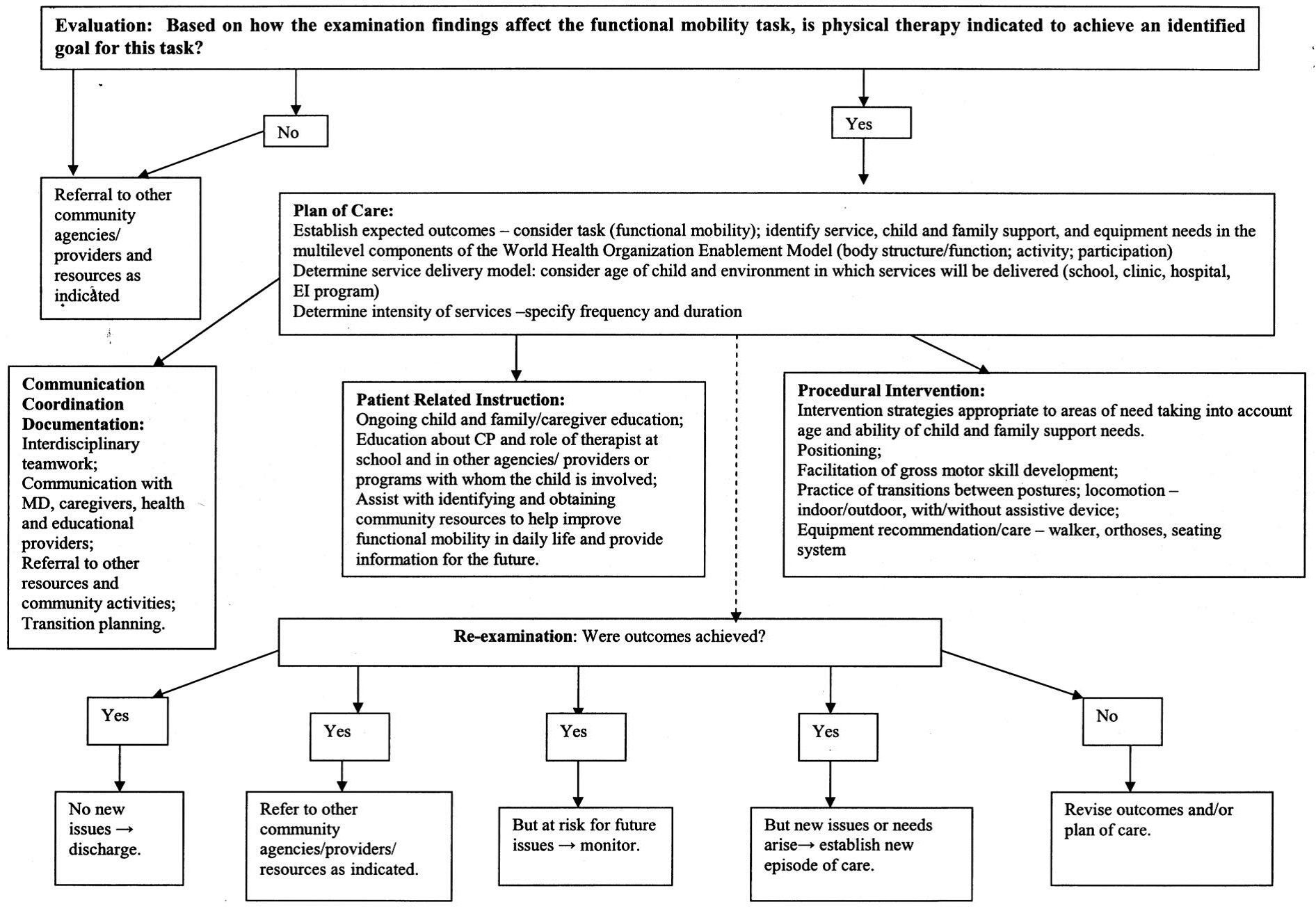
Appraised by: Amanda Fulmer, DPT, October 2014, as part of the Best Practices & Clinical Innovation Committee. Recommend for clinical management be revised periodically to reflect the current literature and new trends in medical and rehab management of children with spastic diplegia.
Additional Resources
Cerebral Palsy Clinical Practice Guideline
Articles of Interest
Masse LC, Schiariti V, et al. Identifying relevant areas of functioning in children and youth with Cerebral Palsy using the ICF-CY coding system: From whose perspective? European Journal of Paediatric Neurology 2014; 609-617.
Physical Therapy Clinical Management Recommendations for Children with Cerebral Palsy –
Spastic Diplegia: Achieving Functional Mobility Outcomes - Examination of functional mobility

